Discount up to 35% for first purchase only this month.
A conceptual framework known as the OSI (Open Systems Interconnection) model divides a communication system’s functionalities into seven separate levels. These tiers specify the network transmission of data. Let’s examine each OSI model layer in detail.
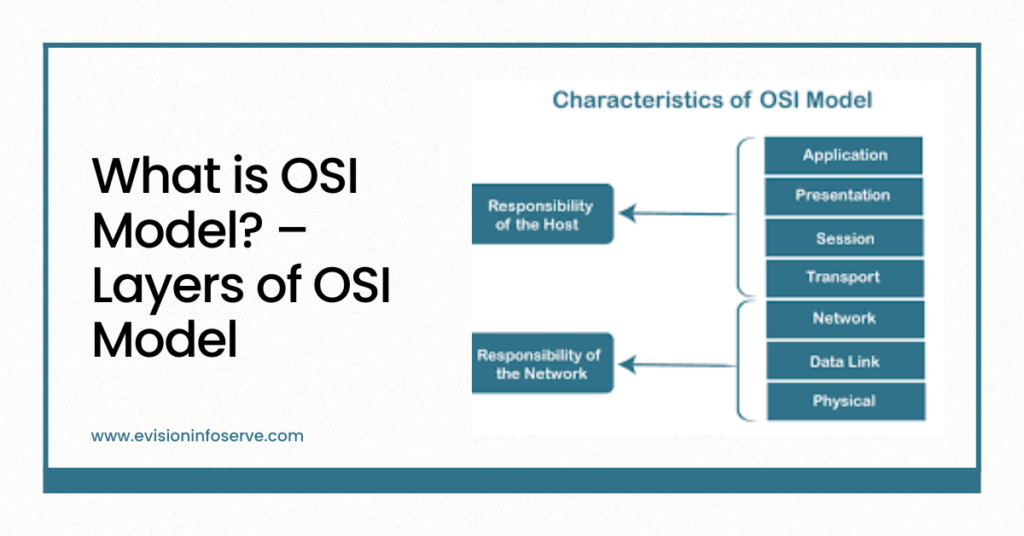
The OSI model is a conceptual framework that standardizes the functions of a communication system. It helps in understanding and designing a network architecture that is robust, interoperable, and scalable. The model divides the communication process into seven logical layers, each responsible for specific tasks in data transmission.
There are seven layers in the OSI model, and each has a distinct function. From Layer 1 at the bottom to Layer 7 at the top, let’s examine each layer:
Each layer of the OSI model interacts with the layers directly above and below it. This interaction ensures that data is transmitted efficiently and reliably across the network.
The OSI model provides several benefits in network design and troubleshooting:
“By understanding the OSI model and its layers, network engineers can design, implement, and maintain complex communication systems effectively.Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis, pulvinar dapibus leo.”
The OSI Model Defined
In the OSI reference model, the communications between a computing system are split into seven different abstraction layers: Physical, Data Link, Network, Transport, Session, Presentation, and Application.
The open systems interconnection (OSI) model is a conceptual model created by the International Organization for Standardization which enables diverse communication systems to communicate using standard protocols.
The Full Form Of OSI Model is a Open Systems Interconnection. The OSI is a model that defines the communication duties of a computing system without consideration to its underlying internal structure and technology. This model was produced by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) in 1984.
100% Original product that covered warranty by the vendor.
You have the right to return your orders within 30 days.
Your orders are shipped seamlessly between countries
Your payments are secure with our private security network.
Evisioninfoserve is dedicated to providing high-quality refurbished laptops to our customers. We understand that not everyone can afford brand-new laptops, and we believe in the value of extending the lifespan of technology while offering affordable options.
+91 9205888941
WhatsApp us