Discount up to 35% for first purchase only this month.
A computer network is a group of connected devices to share resources, communicate, and exchange data. It can be as small as two computers in a home or as large as a global network of millions of devices. Wireless signals, cables, or a combination of both usually connect the devices in a network.
Computer networks are vital in today’s digital age. They enable devices like computers and smartphones to connect and communicate, allowing us to share information and resources effortlessly. They underpin the internet, email, and even online shopping. Networks enhance productivity in businesses, making it easier to collaborate and share data. They are crucial for remote work, ensuring people can access company resources from anywhere.
In essence, computer networks make our interconnected world possible, facilitating communication and access to information, which has become fundamental in both our personal and professional lives.
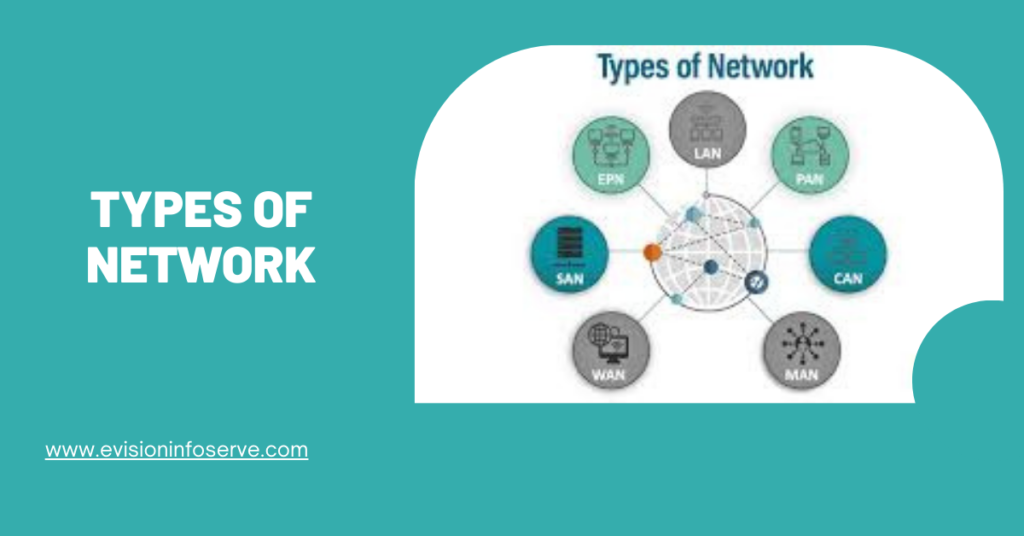
Various types of computer networks are available that serve different purposes, ranging from connecting devices within a small area to connecting devices. Here’s a broad overview of the different computer network components:
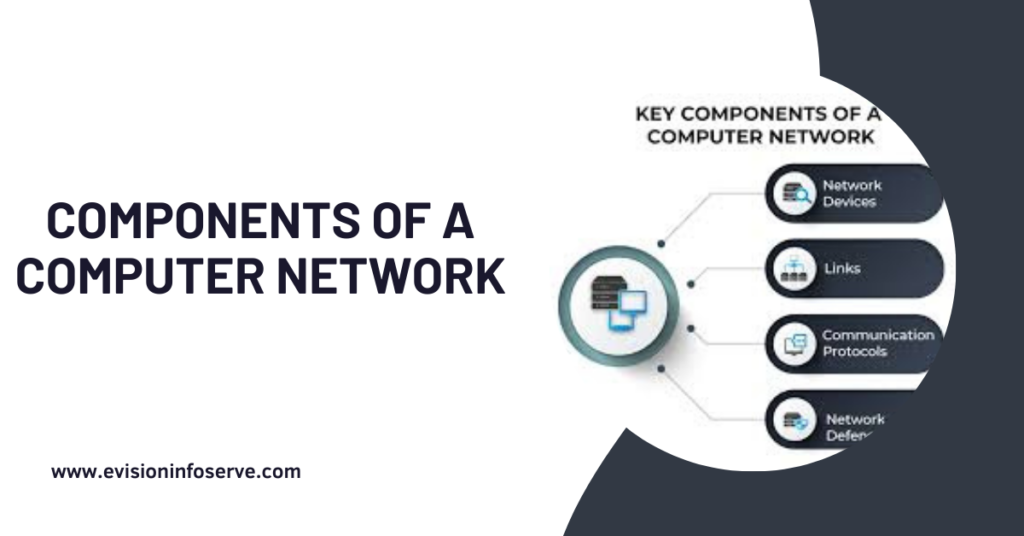
A computer network comprises various components that work together to enable communication and data sharing between devices.
Here’s a broad overview of the different computer network components:
Network devices are tangible tools that facilitate the connection and organization of devices on a network. Such devices include routers, switches, hubs, and access points. These devices play a vital role in allowing devices on the network to communicate by creating a channel for data transmission.
Routers- Routers are networking devices that connect multiple networks and facilitate the exchange of data packets between them. They serve as a gateway between local networks and the internet, allowing devices on the local network to communicate with devices on other networks.
Switches- Switches are networking hardware that provides connectivity between devices connected to a local network. They serve as a bridge for devices to communicate with one another within the same network.
Hubs- A hub is a physical device used in networking that facilitates communication among devices on a local network by directing data packets between them. It is typically employed to extend the reach of a network.
Links are the tangible connections that establish the physical contact between devices on a network. These connections may be through cables or wireless technologies like Ethernet, Wi-Fi, and Bluetooth.
Wired Links- Wired links are connections that utilize cables to join devices on a network. Some common examples of wired links are Ethernet and fiber optic cables.
Wireless Links- Wireless links are connections that use radio waves to connect devices on a network. Examples of wireless links include Wi-Fi and Bluetooth.
Communication protocols are sets of established rules and standards that enable devices to communicate with each other on a network. They determine the format, sequence, and timing of data transmission between devices and how they are identified and errors detected as well as corrected. Some common communication protocols are TCP/IP, HTTP, and FTP.
Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol (TCP/IP)- TCP/IP is a commonly used communication protocol on the internet that provides a set of rules for how data is sent and received between devices and how devices are identified on the network.
HyperText Transfer Protocol (HTTP)- HTTP is a communication protocol that transfers data on the World Wide Web. It enables the transmission and receipt of web pages and other resources by facilitating the exchange of information between devices.
File Transfer Protocol (FTP)- FTP is the protocol used to transfer files between devices on a network.
Network defense refers to the security measures put in place to protect a network from unauthorized access and attacks. Some common types of network defense include:
Firewalls- Firewalls are physical devices that monitor and regulate network traffic flow, both inbound and outbound. Their primary function is to prevent unauthorized access and keep malicious software out of a network.
Intrusion Detection Systems- IDS, or Intrusion Detection Systems, are hardware or software tools that monitor network traffic to detect suspicious or unauthorized activity. Their primary purpose is to alert network administrators of potential security breaches so that they can take appropriate actions.
Virtual Private Networks (VPNs)- Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) are connections established between devices on a network, which use encryption to ensure data protection as it is transmitted over the internet. This encrypted connection allows for a secure exchange of confidential information between devices without the risk of interception or unauthorized access.
“To sum it up, the computer network has transformed how we communicate and interact with technology, making our lives more connected and convenient. However, this connectivity also increases the risk of cyber threats, making it crucial to implement strong security measures such as using complex passwords and keeping software up to date”.
Two basic network types are local-area networks (LANs) and wide-area networks (WANs). LANs connect computers and peripheral devices in a limited physical area, such as a business office, laboratory, or college campus, by means of links (wires, Ethernet cables, fibre optics, Wi-Fi) that transmit data rapidly.
Networking is the process of making connections and building relationships. These connections can provide you with advice and contacts, which can help you make informed career decisions. Networking can even help you find unadvertised jobs/internships. Networking can take place in a group or one-on-one setting.
100% Original product that covered warranty by the vendor.
You have the right to return your orders within 30 days.
Your orders are shipped seamlessly between countries
Your payments are secure with our private security network.
Evisioninfoserve is dedicated to providing high-quality refurbished laptops to our customers. We understand that not everyone can afford brand-new laptops, and we believe in the value of extending the lifespan of technology while offering affordable options.
+91 9205888941
WhatsApp us